pyfst: OpenFst in Python¶
pyfst provides a Python interface to the excellent OpenFst library. Most of the essential functionality of the library is exposed through a simplified API, allowing quick prototyping of algorithms using finite-state methods and easy visual debugging of the results obtained by applying FST operations.
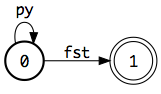
For example, one might write the following code to produce the pyfst logo:
import fst
# Create a first linear chain for 'py', and take its Kleen closure
a = fst.linear_chain(('py',)).closure()
# Create a second acceptor for 'fst'
b = fst.Acceptor(a.isyms)
b.add_arc(0, 1, 'fst')
b[1].final = True
# Concatenate the two transducers
c = a + b
# Remove ε-transitions and minimize
c.remove_epsilon()
c.minimize()
pyfst focuses on providing an intuitive interface to the OpenFst API and lacks support for advanced functionality such as custom semirings and non-vector FST types. However, most operations are available for standard transducers with log and tropical weights, which should be enough for the majority of basic use cases.